-40%
1857 Coast Survey Chart Carquinez Straits California Vallejo City Old Navy Yard
$ 66
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
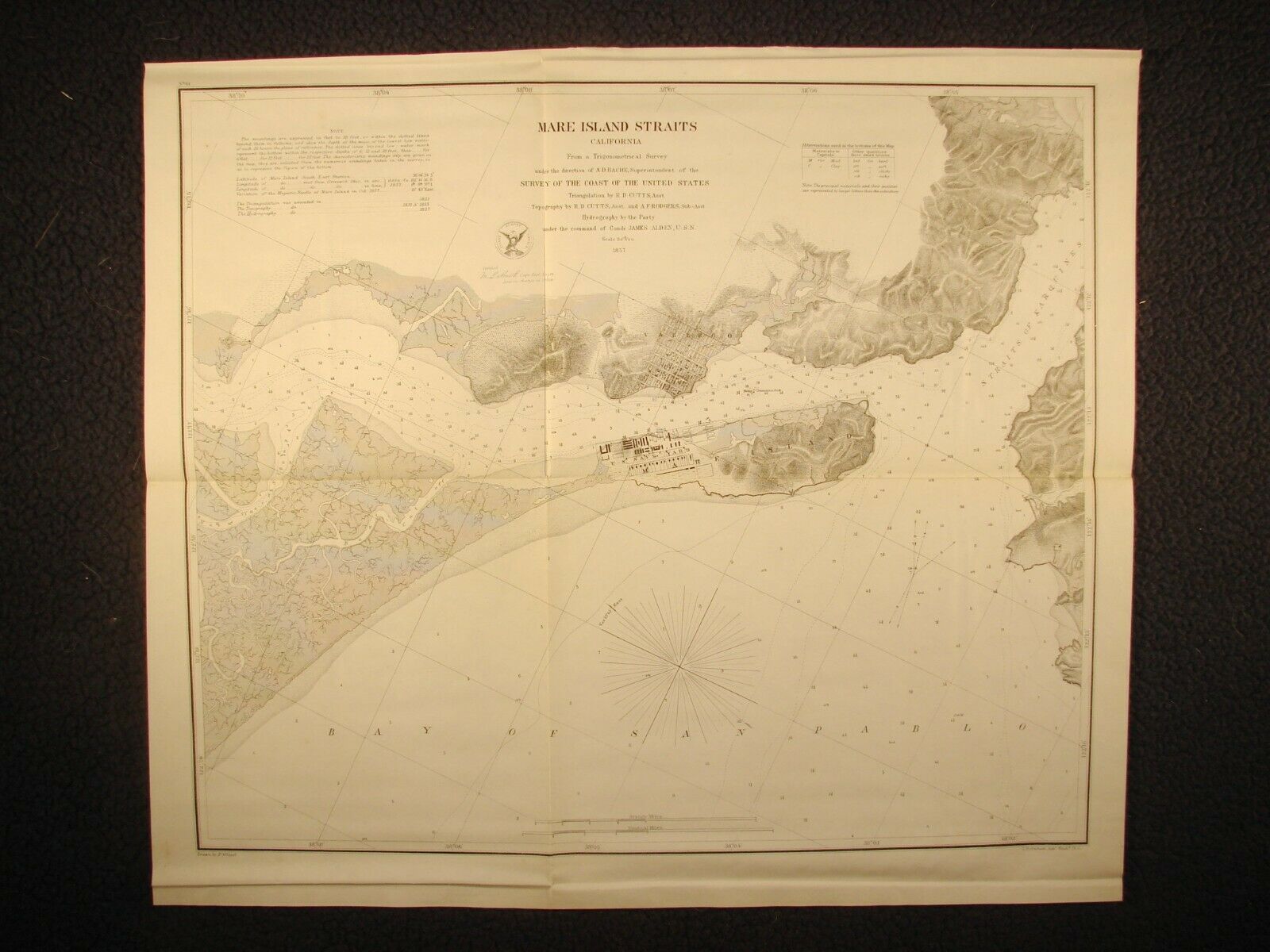
Mare Island Straits, CaliforniaFrom a Trigonometrical Survey under the direction of A. D. Bache, Superintendent of the Survey of the Coast of the United States, Triangulation by R. D. Cutts Asst., Topography by R. D. Cutts Asst. and A. F. Rodgers Sub-Asst., Hydrography by the Party under the Command of Comdg. James Alden, U. S. N.
1857. Drawn by P. Witzel, lithography by C. B. Graham, Washington.
Original lithograph transferred from an engraved copper plate, folded and uncolored, as issued, on thin paper.
Source: Removed from Report of the Coast Survey for the Year 1857.
Size: 14 1/4 x 17 inches (borders); 16 x 18 1/2 inches (sheet)
North oriented to the left top corner.
Scale 1:30,000.
Condition: Faint even age toning with slightly darker toning to fold lines, though less dark than often encountered for Coast Survey annual report maps. There is also a small toning spot or two mentioned for accuracy. Fortunately, the chart seems to have experienced little use, if any, as there are no tears or fold separations. This is a “raw” map which has not been treated, mounted, specially flattened or colored in any way. Overall, a very nice example of this seldom offered and historic chart.
(Note: Although examples with modern hand color are sometimes offered for sale, early charts published by the Coast Survey were originally issued uncolored so it is my preference to offer them that way, thus allowing the new owner the option of leaving the chart in its natural uncolored state or having it professionally colored to specification.)
Early, essentially complete harbor chart of Vallejo, Mare Island and vicinity published by the Coast Survey
A wonderfully detailed, finely drawn and uncommon, small format, preliminary harbor chart (see
About Coast Survey Charts and Types
below) of Vallego (Vallejo) and Mare Island including portions of the areas of present-day Crockett and Rodeo shown in their native state prior to development of these communities. Notes on soundings and abbreviations for bottom materials are given at the top left corner of the chart.
Alternatively called a finished map or preliminary chart in the 1857 annual report, it lacks the usual detailed notes on sailing directions and tides typical of most preliminary harbor charts but, for the first time, shows detail of the young town. In his 1856 report to Superintendent Bache, topographer A. F. Rodgers notes “The town of Vallejo has within the past year assumed the appearance of a thriving place, having now a population of about eight hundred souls”. (Why Vallejo is incorrectly spelled ‘Vallego’ on the chart but correctly as Vallejo in the annual report is unknown. ‘Vallego’ would continue at least into the next edition.) An earlier sketch of Mare Island Straits appeared in 1851 showing “Site of Vallejo – Seat of Government of California” but no streets or buildings. This 1857 preliminary edition was superseded by a finished edition in 1859 with minor changes to naval yard building shading, wetlands patterning, latitude/longitude lettering, and magnetic needle variation. The engraving work was credited to C. T. Klakring.
According to Survey records, further early editions at the same scale appeared in 1861, 1863 and possibly others, reflecting the importance of the straits to commerce and Navy Yard operations.
This beautifully drawn map is distinguished by highly detailed near-shore topography and hydrography including the city waterfront and street grid; individual buildings; shorelines; creeks; marshes; docks; soundings; symbols for identifying character of the bottom, etc., all as they existed in 1855 (topography) and 1857 (hydrography). Low-lying areas are differentiated by various patterns of land use with hilly areas depicted by dense hachuring. Of special historical interest, the U. S. Navy Yard (Mare Island Naval Shipyard) with its many buildings and mouth of the Straits of Karquines (Carquinez) are shown. Who knows what other features will spark your interest!
The detail on the chart is all the more remarkable when one considers that every line, letter, and pattern down to the smallest sand dot was engraved using hand tools by a master engraver
in reverse
(as a mirror image) which happened only after many years of manual field surveying, office computation, drafting, preparation of preliminary illustrations, error checking, revisions, etc. of countless bits of diverse data filling many logbooks and computation volumes. For instance, the soundings alone shown on the chart are numerous, but these are only representative examples selected from the many more that were actually taken during the field surveys and used for chart preparation. In times such as this when one is able to instantaneously pull up an accurate and up-to-date map effortlessly on a pocket cell phone for any location in the country, it is easy to forget the enormous amount of manual effort, work, conditions and sacrifice that early charts and maps such as this required for production. While these early charts have a rigorously sound scientific and engineering basis and purpose, they are also genuine works of art brought to life by a small number of artists and printing professionals possessing exceptional skill and dedication to their craft.
About Coast Survey Charts and Types
Accurate charts and maps of America’s coastline issued by the Coast Survey (later Coast and Geodetic Survey) during the last half of the nineteenth century - many covering areas in detail for the first time - were essential for commerce, communication and national defense. A large variety were published in annual reports during the 1850s-1870s as a means of quickly providing the latest surveyed near-shore topographic and hydrographic information to mariners and the public and are the printings most often encountered in the marketplace. This fortunate circumstance means that many beautiful and historic charts over 150 years old, which otherwise would be rare and expensive as separately issued publications, can be acquired and appreciated at a comparatively lower price. For coastal areas, they are valuable records of our development as a nation which are made all the more interesting to those individuals having a personal connection with an image, time period or place.
Around the time of publication of this chart, the U. S. Coast Survey initiated a new system of product development that divided the main objective of survey cartographic efforts - maps and charts for navigation - into three styles of execution that reflected relative degrees of surveying and information certainty and finish:
1)
Sketches were often the earliest and least detailed or complete type of illustration and consisted of two kinds: a) progress sketches, which showed the year to year progress of the survey work, and b) sketches of selected parts of the coast, either connected or detached, of bays, sounds, harbors, rivers, shoals, channels, capes, etc., based on reconnaissance or regular surveys, which were of variable scales and sizes. Progress sketches were published mainly in annual reports and are of interest for following the serial progression of triangulation surveys, which can be quite intricate, or other types of work. The latter kind were issued for limited nautical use as soon as possible after field surveys but can be quite detailed and contain much information of historical interest, though less appropriate for navigation than illustrations in the preliminary chart class. Generally, sketches were prepared by lower class engravers or apprentices depending upon the level of detail required.
2)
Preliminary charts were a higher quality level of product issued as soon as possible after field surveys, in whole or part, had been made and were used to supply the pressing demands of navigation, pending the completion and publication of finished charts. They differed from finished charts by the amount of information given but not in regard to the correctness of what was given. These charts were usually prepared by lower class engravers known as second and third-class engravers and were also known as second-class charts. For whatever reason, many preliminary charts never reached a finished state prior to the issuance of newer editions based on later resurveys and thus represent the best chart available for the period. This class and some sketches were separately offered for public sale either as engravings or lithographic transfers. Today, they are most often found as lithographs on thin paper provided in the annual reports.
3)
Finished charts, which embodied all information furnished by the survey, included the minutest details of the hydrography and near-shore topography for use by the mariner. Charts of this class were prepared by the survey’s most skilled engravers, known as first-class engravers, and were also known as first-class charts. They were the final product offered for sale to the public and represent the culmination of many years-worth of painstaking effort to provide a complete and high-quality depiction of navigational aids and hazards for the prescribed uses and scales. As a result, finished charts are often among the most beautiful and informative illustrations published by the Coast Survey. They were issued separately for sale as engravings on heavy paper but some were published in the annual reports as lithographic transfers on thin paper.
In practice, this classification scheme is sometimes flexible and muddled, such as reference to a Finished Map class in the annual reports, but the three-class system described above is the one adopted by the Coast Survey for use in its early catalogues of chart and map publications.
Charts were further categorized by scale and use, including the following major types:
1)
General coast or off-shore charts that traced the shoreline over large areas and showed general topographic features but omitted minute details while giving soundings to at least a depth of 120 fathoms to present a general idea of the bottom. Scale 1:400,000
2)
Coast or in-shore charts embracing the shoreline and showing topography of the interior to the nearest main road paralleling the shore with hydrography depicted some 14 miles from shore at a scale of 1:80,000. These charts would enable a navigator to utilize the channels for entering the larger bays and harbors and recognize the beacon, buoys and light-houses by their distinctive features and positions. Preliminary sea coast charts, at a scale of 1:200,000, also served temporarily as in-shore charts pending completion of the regular and more complete series of charts at the 1:80,000 scale.
3)
Harbor charts, on large scales, were intended to meet the needs of local navigation. Scales for these types of charts generally fell within the 1:5,000 to 1:80,000 range and present in minute detail the soundings, bottom characteristics, tides, currents, outlines of the shore, topography of the landings and country adjacent to the shore and inward to the nearest land communication.